Fit Euler diagrams (a generalization of Venn diagrams) using numerical optimization to find exact or approximate solutions to a specification of set relationships. The shape of the diagram may be a circle or an ellipse.
Usage
euler(combinations, ...)
# Default S3 method
euler(
combinations,
input = c("disjoint", "union"),
shape = c("circle", "ellipse"),
loss = c("square", "abs", "region"),
loss_aggregator = c("sum", "max"),
control = list(),
...
)
# S3 method for class 'data.frame'
euler(
combinations,
weights = NULL,
by = NULL,
sep = "_",
factor_names = TRUE,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'matrix'
euler(combinations, ...)
# S3 method for class 'table'
euler(combinations, ...)
# S3 method for class 'list'
euler(combinations, ...)Arguments
- combinations
set relationships as a named numeric vector, matrix, or data.frame (see methods (by class))
- ...
arguments passed down to other methods
- input
type of input: disjoint identities (
'disjoint') or unions ('union').- shape
geometric shape used in the diagram
- loss
type of loss to minimize over. If
"square"is used together with the value"sum"forloss_aggregator, then the resulting loss function is the sum of squared errors, which is the default.- loss_aggregator
how the final loss is computed.
"sum"indicates that the sum of the losses computed bylossare summed up."max"indicates- control
a list of control parameters.
extraopt: should the more thorough optimizer (currentlyGenSA::GenSA()) kick in (providedextraopt_thresholdis exceeded)? The default isTRUEfor ellipses and three sets andFALSEotherwise.extraopt_threshold: threshold, in terms ofdiagError, for when the extra optimizer kicks in. This will almost always slow down the process considerably. A value of 0 means that the extra optimizer will kick in if there is any error. A value of 1 means that it will never kick in. The default is0.001.extraopt_control: a list of control parameters to pass to the extra optimizer, such asmax.call. SeeGenSA::GenSA().
- weights
a numeric vector of weights of the same length as the number of rows in
combinations.- by
a factor or character matrix to be used in
base::by()to split the data.frame or matrix of set combinations- sep
a character to use to separate the dummy-coded factors if there are factor or character vectors in 'combinations'.
- factor_names
whether to include factor names when constructing dummy codes
Value
A list object of class 'euler' with the following parameters.
- ellipses
a matrix of
handk(x and y-coordinates for the centers of the shapes), semiaxesaandb, and rotation anglephi- original.values
set relationships in the input
- fitted.values
set relationships in the solution
- residuals
residuals
- regionError
the difference in percentage points between each disjoint subset in the input and the respective area in the output
- diagError
the largest
regionError- stress
normalized residual sums of squares
Details
If the input is a matrix or data frame and argument by is specified,
the function returns a list of euler diagrams.
The function minimizes the residual sums of squares,
$$
\sum_{i=1}^n (A_i - \omega_i)^2,
$$
by default, where \(\omega_i\) the size of the ith disjoint subset, and
\(A_i\) the corresponding area in the diagram, that is, the unique
contribution to the total area from this overlap. The loss function
can, however, be controlled via the loss argument.
euler() also returns stress (from venneuler), as well as
diagError, and regionError from eulerAPE.
The stress statistic is computed as
$$ \frac{\sum_{i=1}^n (A_i - \beta\omega_i)^2}{\sum_{i=1}^n A_i^2}, $$ where $$ \beta = \sum_{i=1}^n A_i\omega_i / \sum_{i=1}^n \omega_i^2. $$
regionError is computed as
$$ \left| \frac{A_i}{\sum_{i=1}^n A_i} - \frac{\omega_i}{\sum_{i=1}^n \omega_i}\right|. $$
diagError is simply the maximum of regionError.
Methods (by class)
euler(default): a named numeric vector, with combinations separated by an ampersand, for instanceA&B = 10. Missing combinations are treated as being 0.euler(data.frame): adata.frameof logicals, binary integers, or factors.euler(matrix): a matrix that can be converted to a data.frame of logicals (as in the description above) viabase::as.data.frame.matrix().euler(table): A table withmax(dim(x)) < 3.euler(list): a list of vectors, each vector giving the contents of that set (with no duplicates). Vectors in the list must be named.
References
Wilkinson L. Exact and Approximate Area-Proportional Circular Venn and Euler Diagrams. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (Internet). 2012 Feb (cited 2016 Apr 9);18(2):321-31. Available from: doi:10.1109/TVCG.2011.56
Micallef L, Rodgers P. eulerAPE: Drawing Area-Proportional 3-Venn Diagrams Using Ellipses. PLOS ONE (Internet). 2014 Jul (cited 2016 Dec 10);9(7):e101717. Available from: doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0101717
Examples
# Fit a diagram with circles
combo <- c(A = 2, B = 2, C = 2, "A&B" = 1, "A&C" = 1, "B&C" = 1)
fit1 <- euler(combo)
# Investigate the fit
fit1
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> A 2 2.076 -0.076 0.021
#> B 2 2.076 -0.076 0.021
#> C 2 2.076 -0.076 0.021
#> A&B 1 0.605 0.395 0.040
#> A&C 1 0.605 0.395 0.040
#> B&C 1 0.605 0.395 0.040
#> A&B&C 0 0.494 -0.494 0.058
#>
#> diagError: 0.058
#> stress: 0.049
# Refit using ellipses instead
fit2 <- euler(combo, shape = "ellipse")
# Investigate the fit again (which is now exact)
fit2
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> A 2 2 0 0
#> B 2 2 0 0
#> C 2 2 0 0
#> A&B 1 1 0 0
#> A&C 1 1 0 0
#> B&C 1 1 0 0
#> A&B&C 0 0 0 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# Plot it
plot(fit2)
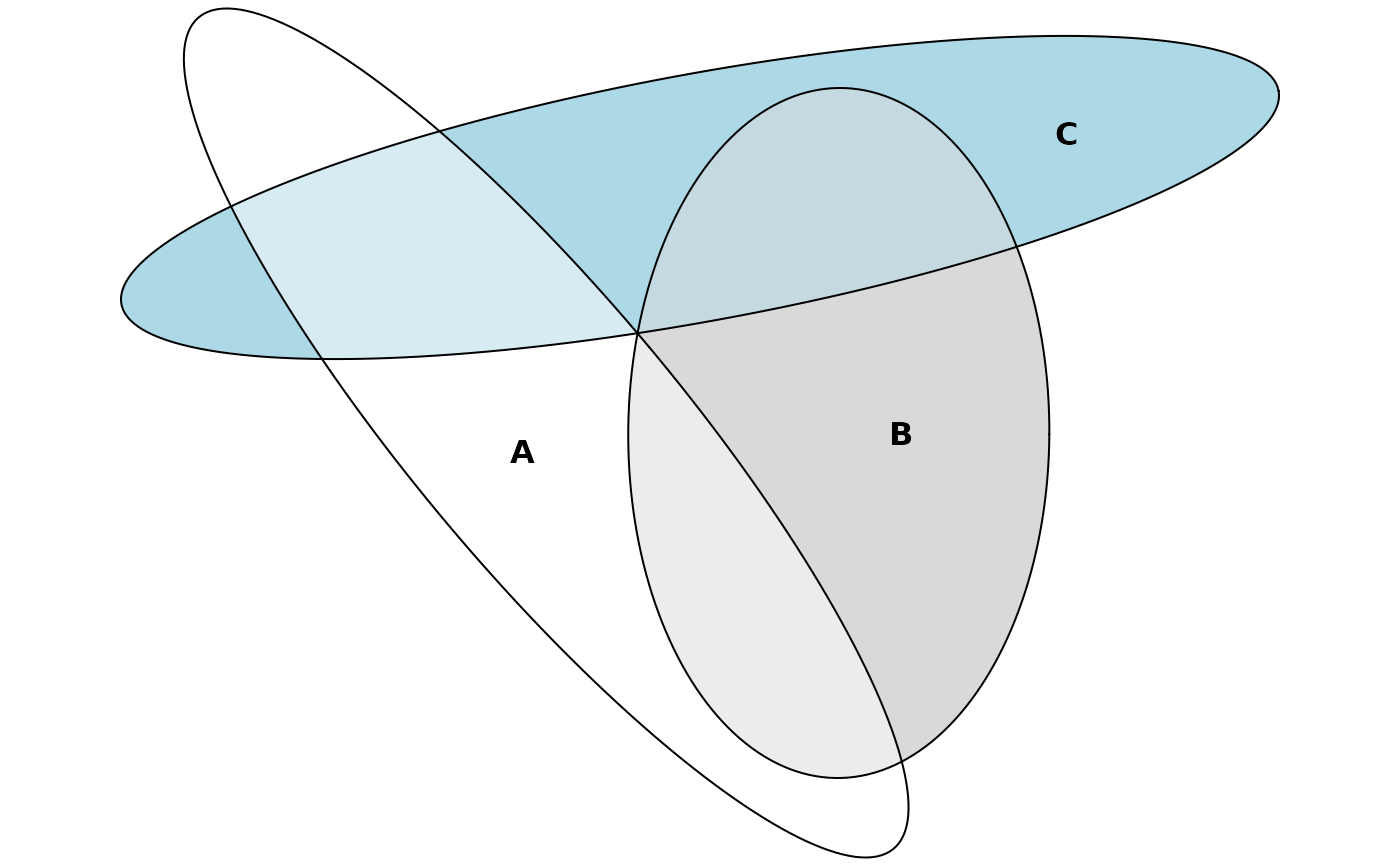 # A set with no perfect solution
euler(c(
"a" = 3491, "b" = 3409, "c" = 3503,
"a&b" = 120, "a&c" = 114, "b&c" = 132,
"a&b&c" = 50
))
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> a 3491 3491 0 0.001
#> b 3409 3409 0 0.001
#> c 3503 3503 0 0.002
#> a&b 120 120 0 0.000
#> a&c 114 114 0 0.000
#> b&c 132 132 0 0.000
#> a&b&c 50 0 50 0.005
#>
#> diagError: 0.005
#> stress: 0
# Using grouping via the 'by' argument through the data.frame method
euler(fruits, by = list(sex, age))
#> female.adult
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 1 0.937 0.063 0.009
#> apple 2 1.968 0.032 0.009
#> orange 2 1.974 0.026 0.009
#> banana&apple 4 4.028 -0.028 0.010
#> banana&orange 0 0.268 -0.268 0.024
#> apple&orange 0 0.260 -0.260 0.023
#> banana&apple&orange 2 1.961 0.039 0.010
#>
#> diagError: 0.024
#> stress: 0.005
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.child
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 3 2.994 0.006 0.003
#> apple 1 0.982 0.018 0.002
#> orange 1 0.981 0.019 0.002
#> banana&apple 10 10.004 -0.004 0.007
#> banana&orange 0 0.137 -0.137 0.008
#> apple&orange 0 0.144 -0.144 0.008
#> banana&apple&orange 3 2.993 0.007 0.003
#>
#> diagError: 0.008
#> stress: 0
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.adult
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 3 3.000 0.000 0.000
#> apple 2 2.003 -0.003 0.000
#> orange 0 0.016 -0.016 0.001
#> banana&apple 10 10.000 0.000 0.001
#> banana&orange 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> apple&orange 1 0.996 0.004 0.000
#> banana&apple&orange 1 1.002 -0.002 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.001
#> stress: 0
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> female.child
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 4 4 0 0
#> apple 0 0 0 0
#> orange 1 1 0 0
#> banana&apple 4 4 0 0
#> banana&orange 1 1 0 0
#> apple&orange 0 0 0 0
#> banana&apple&orange 2 2 0 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# Using the matrix method
euler(organisms)
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> animal 0 0.582 -0.582 0.086
#> mammal 0 0.302 -0.302 0.044
#> plant 0 0.210 -0.210 0.031
#> sea 0 0.430 -0.430 0.063
#> spiny 0 0.166 -0.166 0.025
#> animal&mammal 2 1.817 0.183 0.018
#> animal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea 1 0.612 0.388 0.053
#> animal&spiny 0 0.215 -0.215 0.032
#> mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea 1 0.000 1.000 0.143
#> mammal&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea 1 0.868 0.132 0.015
#> plant&spiny 1 0.000 1.000 0.143
#> sea&spiny 0 0.176 -0.176 0.026
#> animal&mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea 0 0.268 -0.268 0.040
#> animal&mammal&spiny 0 0.061 -0.061 0.009
#> animal&plant&sea 0 0.119 -0.119 0.018
#> animal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea&spiny 1 0.715 0.285 0.037
#> mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea&spiny 0 0.016 -0.016 0.002
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.177 -0.177 0.026
#> animal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.043 -0.043 0.006
#> mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.143
#> stress: 0.352
# Using weights
euler(organisms, weights = c(10, 20, 5, 4, 8, 9, 2))
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> animal 0 0.789 -0.789 0.019
#> mammal 0 0.360 -0.360 0.009
#> plant 0 0.099 -0.099 0.002
#> sea 0 0.409 -0.409 0.010
#> spiny 0 0.200 -0.200 0.005
#> animal&mammal 30 29.984 0.016 0.197
#> animal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea 4 0.169 3.831 0.065
#> animal&spiny 0 0.027 -0.027 0.001
#> mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea 8 0.000 8.000 0.138
#> mammal&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea 2 0.000 2.000 0.034
#> plant&spiny 9 9.000 0.000 0.059
#> sea&spiny 0 0.062 -0.062 0.001
#> animal&mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea 0 0.431 -0.431 0.010
#> animal&mammal&spiny 0 0.100 -0.100 0.002
#> animal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&plant&spiny 0 0.176 -0.176 0.004
#> animal&sea&spiny 5 0.018 4.982 0.086
#> mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea&spiny 0 0.098 -0.098 0.002
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.054 -0.054 0.001
#> animal&mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.002 -0.002 0.000
#> mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.197
#> stress: 0.1
# The table method
euler(pain, factor_names = FALSE)
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> widespread 204 204.002 -0.002 0
#> regional 229 229.002 -0.002 0
#> male 48 48.032 -0.032 0
#> widespread®ional 0 0.000 0.000 0
#> widespread&male 78 77.984 0.016 0
#> regional&male 143 142.992 0.008 0
#> widespread®ional&male 0 0.247 -0.247 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# A euler diagram from a list of sample spaces (the list method)
euler(plants[c("erigenia", "solanum", "cynodon")])
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> erigenia 0 0 0 0
#> solanum 16 16 0 0
#> cynodon 1 1 0 0
#> erigenia&solanum 2 2 0 0
#> erigenia&cynodon 0 0 0 0
#> solanum&cynodon 25 25 0 0
#> erigenia&solanum&cynodon 20 20 0 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# A set with no perfect solution
euler(c(
"a" = 3491, "b" = 3409, "c" = 3503,
"a&b" = 120, "a&c" = 114, "b&c" = 132,
"a&b&c" = 50
))
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> a 3491 3491 0 0.001
#> b 3409 3409 0 0.001
#> c 3503 3503 0 0.002
#> a&b 120 120 0 0.000
#> a&c 114 114 0 0.000
#> b&c 132 132 0 0.000
#> a&b&c 50 0 50 0.005
#>
#> diagError: 0.005
#> stress: 0
# Using grouping via the 'by' argument through the data.frame method
euler(fruits, by = list(sex, age))
#> female.adult
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 1 0.937 0.063 0.009
#> apple 2 1.968 0.032 0.009
#> orange 2 1.974 0.026 0.009
#> banana&apple 4 4.028 -0.028 0.010
#> banana&orange 0 0.268 -0.268 0.024
#> apple&orange 0 0.260 -0.260 0.023
#> banana&apple&orange 2 1.961 0.039 0.010
#>
#> diagError: 0.024
#> stress: 0.005
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.child
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 3 2.994 0.006 0.003
#> apple 1 0.982 0.018 0.002
#> orange 1 0.981 0.019 0.002
#> banana&apple 10 10.004 -0.004 0.007
#> banana&orange 0 0.137 -0.137 0.008
#> apple&orange 0 0.144 -0.144 0.008
#> banana&apple&orange 3 2.993 0.007 0.003
#>
#> diagError: 0.008
#> stress: 0
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.adult
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 3 3.000 0.000 0.000
#> apple 2 2.003 -0.003 0.000
#> orange 0 0.016 -0.016 0.001
#> banana&apple 10 10.000 0.000 0.001
#> banana&orange 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> apple&orange 1 0.996 0.004 0.000
#> banana&apple&orange 1 1.002 -0.002 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.001
#> stress: 0
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> female.child
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> banana 4 4 0 0
#> apple 0 0 0 0
#> orange 1 1 0 0
#> banana&apple 4 4 0 0
#> banana&orange 1 1 0 0
#> apple&orange 0 0 0 0
#> banana&apple&orange 2 2 0 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# Using the matrix method
euler(organisms)
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> animal 0 0.582 -0.582 0.086
#> mammal 0 0.302 -0.302 0.044
#> plant 0 0.210 -0.210 0.031
#> sea 0 0.430 -0.430 0.063
#> spiny 0 0.166 -0.166 0.025
#> animal&mammal 2 1.817 0.183 0.018
#> animal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea 1 0.612 0.388 0.053
#> animal&spiny 0 0.215 -0.215 0.032
#> mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea 1 0.000 1.000 0.143
#> mammal&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea 1 0.868 0.132 0.015
#> plant&spiny 1 0.000 1.000 0.143
#> sea&spiny 0 0.176 -0.176 0.026
#> animal&mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea 0 0.268 -0.268 0.040
#> animal&mammal&spiny 0 0.061 -0.061 0.009
#> animal&plant&sea 0 0.119 -0.119 0.018
#> animal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea&spiny 1 0.715 0.285 0.037
#> mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea&spiny 0 0.016 -0.016 0.002
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.177 -0.177 0.026
#> animal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.043 -0.043 0.006
#> mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.143
#> stress: 0.352
# Using weights
euler(organisms, weights = c(10, 20, 5, 4, 8, 9, 2))
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> animal 0 0.789 -0.789 0.019
#> mammal 0 0.360 -0.360 0.009
#> plant 0 0.099 -0.099 0.002
#> sea 0 0.409 -0.409 0.010
#> spiny 0 0.200 -0.200 0.005
#> animal&mammal 30 29.984 0.016 0.197
#> animal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&sea 4 0.169 3.831 0.065
#> animal&spiny 0 0.027 -0.027 0.001
#> mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea 8 0.000 8.000 0.138
#> mammal&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea 2 0.000 2.000 0.034
#> plant&spiny 9 9.000 0.000 0.059
#> sea&spiny 0 0.062 -0.062 0.001
#> animal&mammal&plant 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&sea 0 0.431 -0.431 0.010
#> animal&mammal&spiny 0 0.100 -0.100 0.002
#> animal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&plant&spiny 0 0.176 -0.176 0.004
#> animal&sea&spiny 5 0.018 4.982 0.086
#> mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> plant&sea&spiny 0 0.098 -0.098 0.002
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&spiny 0 0.054 -0.054 0.001
#> animal&mammal&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.002 -0.002 0.000
#> mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#> animal&mammal&plant&sea&spiny 0 0.000 0.000 0.000
#>
#> diagError: 0.197
#> stress: 0.1
# The table method
euler(pain, factor_names = FALSE)
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> widespread 204 204.002 -0.002 0
#> regional 229 229.002 -0.002 0
#> male 48 48.032 -0.032 0
#> widespread®ional 0 0.000 0.000 0
#> widespread&male 78 77.984 0.016 0
#> regional&male 143 142.992 0.008 0
#> widespread®ional&male 0 0.247 -0.247 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0
# A euler diagram from a list of sample spaces (the list method)
euler(plants[c("erigenia", "solanum", "cynodon")])
#> original fitted residuals regionError
#> erigenia 0 0 0 0
#> solanum 16 16 0 0
#> cynodon 1 1 0 0
#> erigenia&solanum 2 2 0 0
#> erigenia&cynodon 0 0 0 0
#> solanum&cynodon 25 25 0 0
#> erigenia&solanum&cynodon 20 20 0 0
#>
#> diagError: 0
#> stress: 0