This function fits Venn diagrams using an interface that is
almost identical to euler(). Strictly speaking,
Venn diagrams are Euler diagrams where every intersection is visible,
regardless of whether or not it is zero. In almost every incarnation of
Venn diagrams, however, the areas in the diagram are also
non-proportional to the input; this is also the case here.
Usage
venn(combinations, ...)
# Default S3 method
venn(
combinations,
input = c("disjoint", "union"),
names = letters[length(combinations)],
...
)
# S3 method for class 'table'
venn(combinations, ...)
# S3 method for class 'data.frame'
venn(
combinations,
weights = NULL,
by = NULL,
sep = "_",
factor_names = TRUE,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'matrix'
venn(combinations, ...)
# S3 method for class 'list'
venn(combinations, ...)Arguments
- combinations
set relationships as a named numeric vector, matrix, or data.frame (see methods (by class))
- ...
arguments passed down to other methods
- input
type of input: disjoint identities (
'disjoint') or unions ('union').- names
a character vector for the names of each set of the same length as 'combinations'. Must not be
NULLifcombinationsis a one-length numeric.- weights
a numeric vector of weights of the same length as the number of rows in
combinations.- by
a factor or character matrix to be used in
base::by()to split the data.frame or matrix of set combinations- sep
a character to use to separate the dummy-coded factors if there are factor or character vectors in 'combinations'.
- factor_names
whether to include factor names when constructing dummy codes
Value
Returns an object of class 'venn', 'euler' with items
- ellipses
a matrix of
handk(x and y-coordinates for the centers of the shapes), semiaxesaandb, and rotation anglephi- original.values
set relationships in the input
- fitted.values
set relationships in the solution
Methods (by class)
venn(default): a named numeric vector, with combinations separated by an ampersand, for instanceA&B = 10. Missing combinations are treated as being 0.venn(table): A table withmax(dim(x)) < 3.venn(data.frame): adata.frameof logicals, binary integers, or factors.venn(matrix): a matrix that can be converted to a data.frame of logicals (as in the description above) viabase::as.data.frame.matrix().venn(list): a list of vectors, each vector giving the contents of that set (with no duplicates). Vectors in the list do not need to be named.
Examples
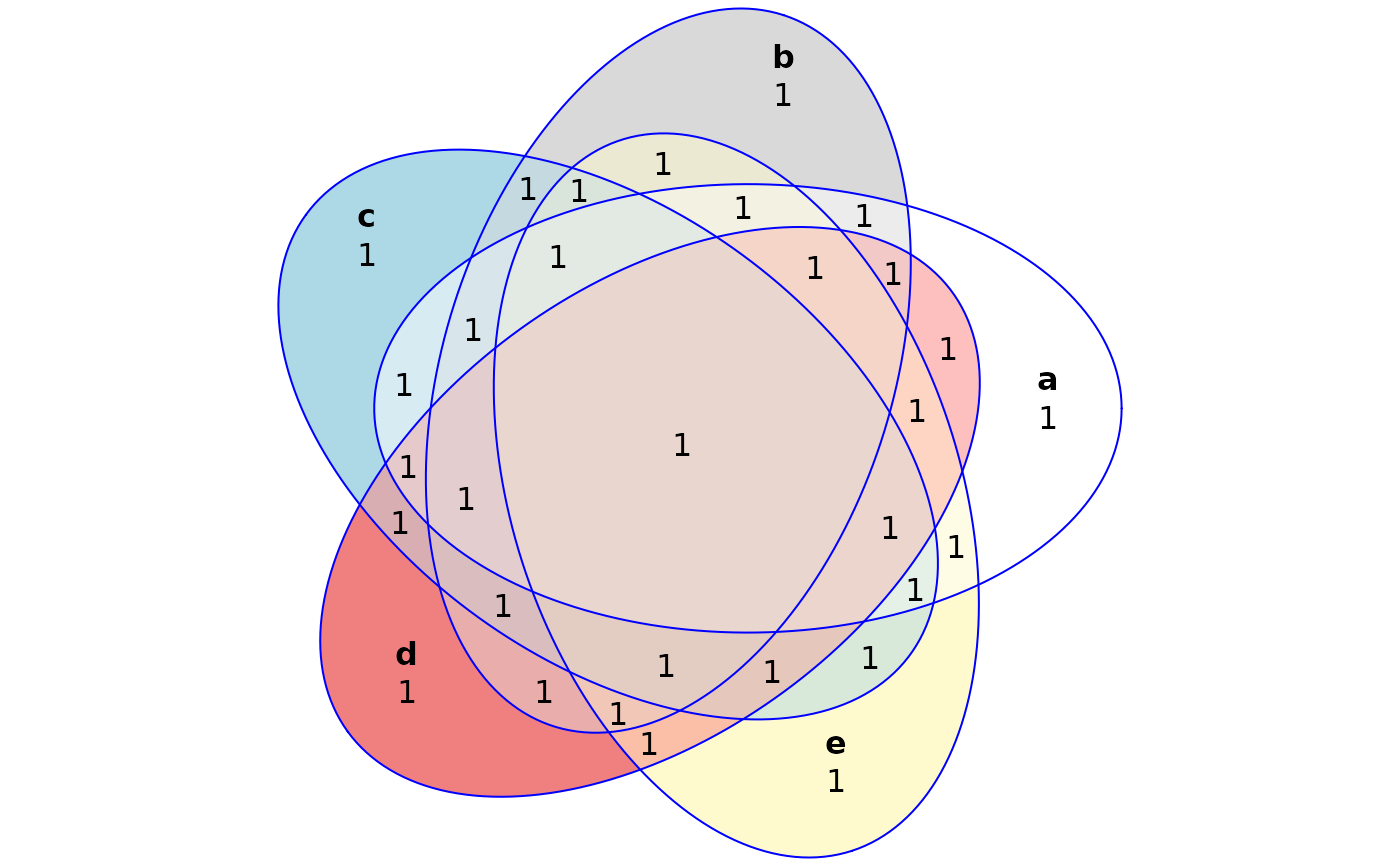
# The trivial version
f1 <- venn(5, names = letters[1:5])
plot(f1)
 # Using data (a numeric vector)
f2 <- venn(c(A = 1, "B&C" = 3, "A&D" = 0.3))
# The table method
venn(pain, factor_names = FALSE)
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> widespread -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> regional 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> male 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
# Using grouping via the 'by' argument through the data.frame method
venn(fruits, by = list(sex, age))
#> female.adult
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.child
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.adult
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> female.child
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
# Using the matrix method
venn(organisms)
#> 5 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> animal 0.176 0.096 1 0.6 0.000
#> mammal -0.037 0.197 1 0.6 1.257
#> plant -0.198 0.026 1 0.6 2.513
#> sea -0.086 -0.181 1 0.6 3.770
#> spiny 0.145 -0.137 1 0.6 5.027
# Using weights
venn(organisms, weights = c(10, 20, 5, 4, 8, 9, 2))
#> 5 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> animal 0.176 0.096 1 0.6 0.000
#> mammal -0.037 0.197 1 0.6 1.257
#> plant -0.198 0.026 1 0.6 2.513
#> sea -0.086 -0.181 1 0.6 3.770
#> spiny 0.145 -0.137 1 0.6 5.027
# A venn diagram from a list of sample spaces (the list method)
venn(plants[c("erigenia", "solanum", "cynodon")])
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> erigenia -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> solanum 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> cynodon 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
# Using data (a numeric vector)
f2 <- venn(c(A = 1, "B&C" = 3, "A&D" = 0.3))
# The table method
venn(pain, factor_names = FALSE)
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> widespread -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> regional 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> male 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
# Using grouping via the 'by' argument through the data.frame method
venn(fruits, by = list(sex, age))
#> female.adult
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.child
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> male.adult
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> ------------------------------------------------------------
#> female.child
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> banana -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> apple 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> orange 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
# Using the matrix method
venn(organisms)
#> 5 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> animal 0.176 0.096 1 0.6 0.000
#> mammal -0.037 0.197 1 0.6 1.257
#> plant -0.198 0.026 1 0.6 2.513
#> sea -0.086 -0.181 1 0.6 3.770
#> spiny 0.145 -0.137 1 0.6 5.027
# Using weights
venn(organisms, weights = c(10, 20, 5, 4, 8, 9, 2))
#> 5 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> animal 0.176 0.096 1 0.6 0.000
#> mammal -0.037 0.197 1 0.6 1.257
#> plant -0.198 0.026 1 0.6 2.513
#> sea -0.086 -0.181 1 0.6 3.770
#> spiny 0.145 -0.137 1 0.6 5.027
# A venn diagram from a list of sample spaces (the list method)
venn(plants[c("erigenia", "solanum", "cynodon")])
#> 3 set Venn diagram
#>
#> h k a b phi
#> erigenia -0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> solanum 0.42 -0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76
#> cynodon 0.00 0.36 1.05 1.05 3.76